3. Irish Creek Riparian Conditions
Shoreline Buffer Land Cover Evaluation
The riparian or shoreline zone is that special area where the land meets the water. Well-vegetated shorelines are critically important in protecting water quality and creating healthy aquatic habitats, lakes and rivers. Natural shorelines intercept sediments and contaminants that could impact water quality conditions and harm fish habitat in streams. Well established buffers protect the banks against erosion, improve habitat for fish by shading and cooling the water and provide protection for birds and other wildlife that feed and rear young near water. A recommended target (from Environment Canada’s Guideline: How Much Habitat is Enough?) is to maintain a minimum 30 metre wide vegetated buffer along at least 75 percent of the length of both sides of rivers, creeks and streams.
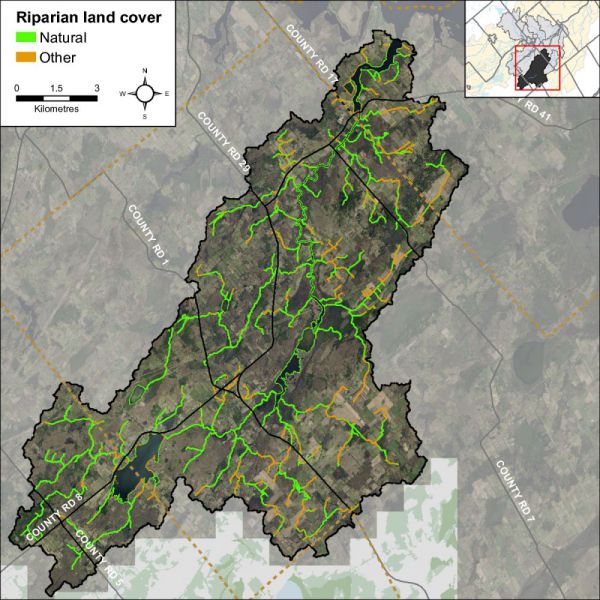
Figure 10 shows the extent of the naturally vegetated riparian zone along a 30 metre deep/wide area of the shoreline of Irish Creek and its tributaries. This information is derived from a dataset developed by the RVCA’s Land Cover Classification Program through heads-up digitization of 20cm DRAPE ortho-imagery at a 1:4000 scale, which details the catchment landscape using 10 land cover classes.
This analysis shows that the riparian buffer in the Irish Creek catchment is comprised of wetland (53 percent), crop and pastureland (25 percent), woodland (18 percent), roads (two percent) and settlement areas (two percent). Additional statistics for the Irish Creek catchment are presented in Table 7 and show that there has been very little change in shoreline cover from 2008 to 2014.
| Riparian Land Cover | 2008 | 2014 | Change - 2008 to 2014 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | Area | Area | ||||
| Ha. | Percent | Ha. | Percent | Ha. | Percent | |
| Wetland | 727 | 53 | 730 | 53 | 3 | |
| > evaluated | (397) | (29) | (397) | (29) | (0) | (0) |
| > unevaluated | (330) | (24) | (333) | (24) | (3) | (0) |
| Crop & Pasture | 349 | 25 | 346 | 25 | -3 | |
| Woodland | 241 | 18 | 240 | 18 | -1 | -1 |
| Transportation | 30 | 2 | 30 | 2 | ||
| Settlement | 25 | 2 | 26 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
Irish Creek Overbank Zone
Riparian Buffer Width Evaluation
Figure 11 demonstrates the buffer conditions of the left and right banks separately. Irish Creek had a buffer of greater than 30 meters along 97 percent of the right bank and 98 percent of the left bank.
Adjacent Land Use
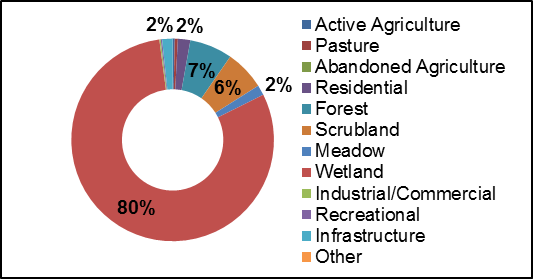
The RVCA’s Stream Characterization Program identifies six different land uses beside Irish Creek (Figure 12). Surrounding land use is considered from the beginning to end of the survey section (100m) and up to 100m on each side of the creek. Land use outside of this area is not considered for the surveys but is nonetheless part of the subwatershed and will influence the creek. Natural areas made up 95 percent of the stream, characterized by wetlands, forest, scrubland and meadow. Wetland habitat was dominant in the adjacent lands along Irish Creek at 80 percent. The remaining land use consisted of residential and infrastructure in the form of road crossings.
Irish Creek Shoreline Zone
Instream Erosion
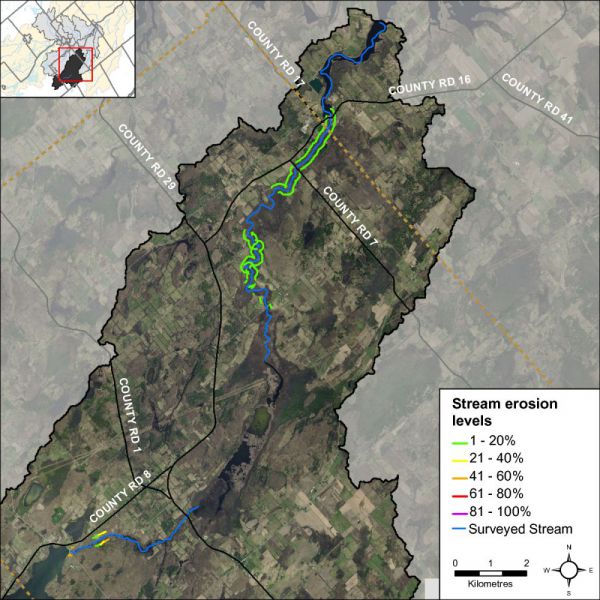
Erosion is a normal, important stream process and may not affect actual bank stability; however, excessive erosion and deposition of sediment within a stream can have a detrimental effect on important fish and wildlife habitat. Poor bank stability can greatly contribute to the amount of sediment carried in a waterbody as well as loss of bank vegetation due to bank failure, resulting in trees falling into the stream and the potential to impact instream migration. Figure 13 shows low levels of erosion along Irish Creek.
Undercut Stream Banks
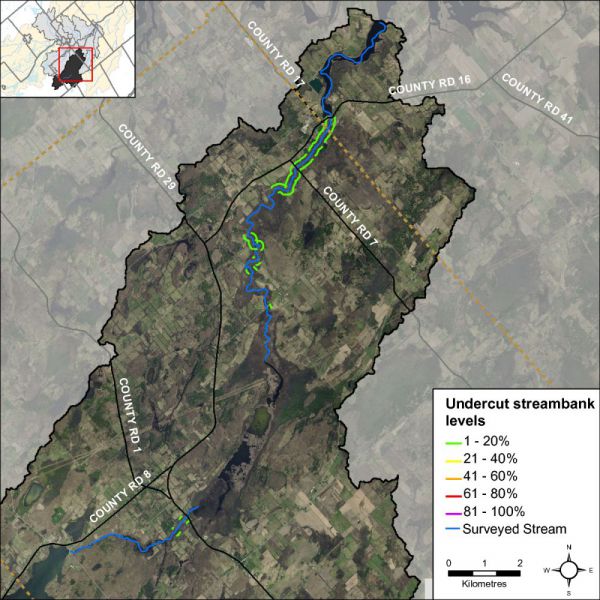
Undercut banks are a normal and natural part of stream function and can provide excellent refuge areas for fish. Figure 14 shows that Irish Creek had low levels of undercut banks along the system.
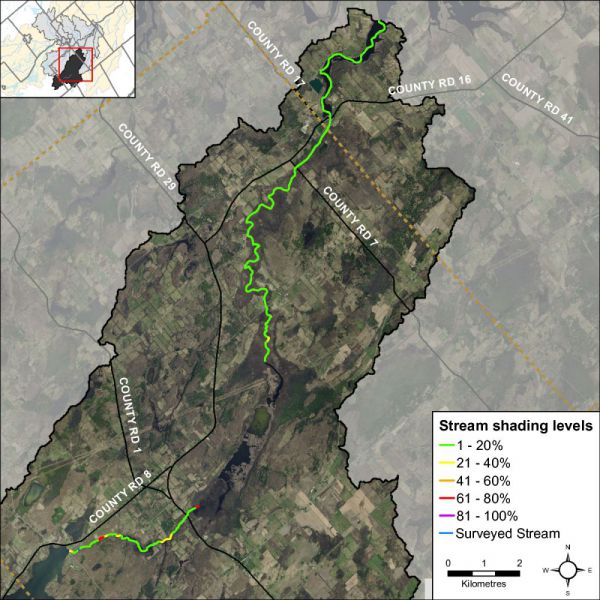
Stream Shading
Grasses, shrubs and trees all contribute towards shading a stream. Shade is important in moderating stream temperature, contributing to food supply and helping with nutrient reduction within a stream. Figure 15 shows low levels of stream shading dominate conditions in most reaches of Irish Creek.
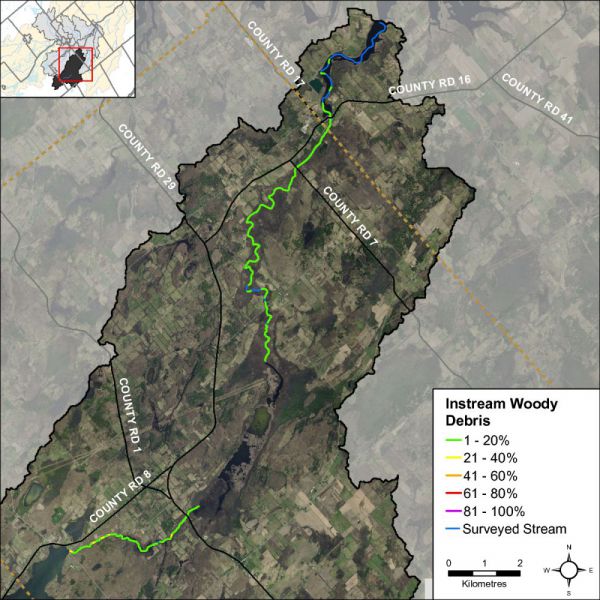
Instream Woody Debris
Figure 16 shows that the majority of Irish Creek had low to moderate levels of instream woody debris in the form of branches and trees. Instream woody debris is important for fish and benthic invertebrate habitat, by providing refuge and feeding areas.
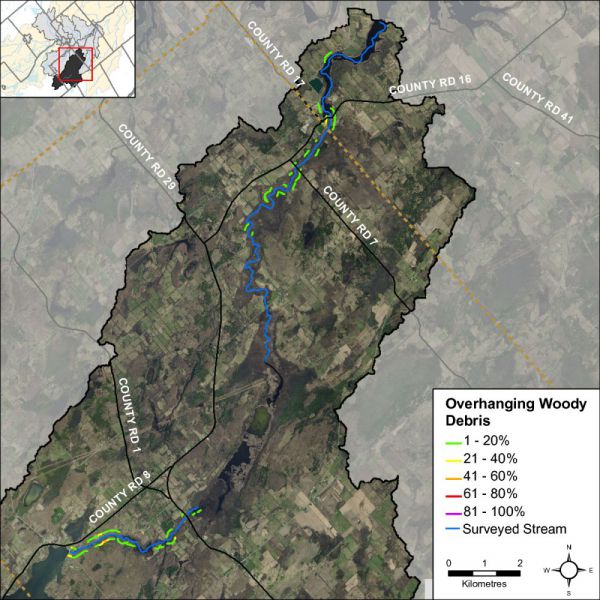
Overhanging Trees and Branches
Figure 17 shows the system is dominated by low to moderate levels of overhanging branches and trees along Irish Creek. Overhanging branches and trees provide a food source, nutrients and shade which helps to moderate instream water temperatures.
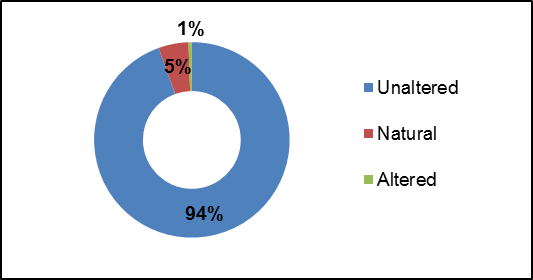
Anthropogenic Alterations
Figure 18 shows 94 percent of Irish Creek remains “unaltered” with no anthropogenic alterations. Five percent of Irish Creek was classified as natural with minor anthropogenic changes and one percent was considered altered in the form of road crossings.
Irish Creek Instream Aquatic Habitat
Benthic Invertebrates
Freshwater benthic invertebrates are animals without backbones that live on the stream bottom and include crustaceans such as crayfish, molluscs and immature forms of aquatic insects. Benthos represent an extremely diverse group of aquatic animals and exhibit wide ranges of responses to stressors such as organic pollutants, sediments and toxicants, which allows scientists to use them as bioindicators. As part of the Ontario Benthic Biomonitoring Network (OBBN), the RVCA has been collecting benthic invertebrates at the Kinch road site on Irish Creek since 2003. Monitoring data is analyzed for each sample site and the results are presented using the Family Biotic Index, Family Richness and percent Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera and Trichoptera.
Hilsenhoff Family Biotic Index
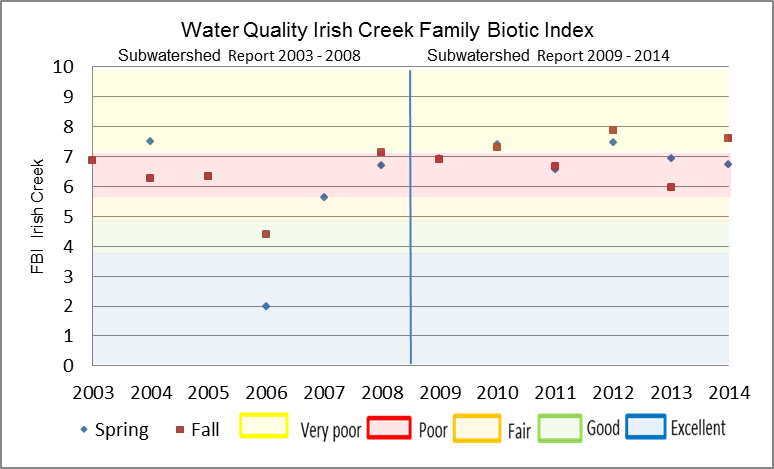
The Hilsenhoff Family Biotic Index (FBI) is an indicator of organic and nutrient pollution and provides an estimate of water quality conditions for each site using established pollution tolerance values for benthic invertebrates. FBI results for Irish Creek are separated by reporting period 2003 to 2008 and 2009 to 2014. “Poor” to “Very poor” water quality conditions being observed at the Irish Creek sample location for the period from 2003 to 2014 (Fig.19) using a grading scheme developed by Conservation Authorities in Ontario for benthic invertebrates.
Family Richness
Family Richness measures the health of the community through its diversity and increases with increasing habitat diversity suitability and healthy water quality conditions. Family Richness is equivalent to the total number of benthic invertebrate families found within a sample. Irish Creek is reported to have “Poor” to “Good” family richness (Fig.20).
EPT
Ephemeroptera (Mayflies), Plecoptera (Stoneflies), and Trichoptera (Caddisflies) are species considered to be very sensitive to poor water quality conditions. High abundance of these organisms is generally an indication of good water quality conditions at a sample location. During more recent sampling years the community structure has been shifting to species that are more sensitive to poor water quality conditions. As a result, the EPT indicates that Irish Creek is reported to have “Poor” water quality (Fig.21) from 2003 to 2014.
Conclusion
Overall Irish Creek aquatic habitat conditions from a benthic invertebrate perspective is considered “Poor” from 2003 to 2014 as the samples are dominated by species that are tolerant of high organic pollution levels.
Habitat Complexity
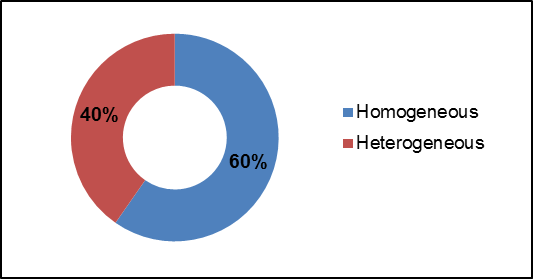
Streams are naturally meandering systems and move over time; there are varying degrees of habitat complexity, depending on the creek. Examples of habitat complexity include variable habitat types such as pools and riffles as well as substrate variability and woody debris structure. A high percentage of habitat complexity (heterogeneity) typically increases the biodiversity of aquatic organisms within a system. Forty percent of Irish Creek was considered heterogeneous, as shown in Figure 22. The majority of the Irish Creek system is classified as a riverine wetland.
Instream Substrate
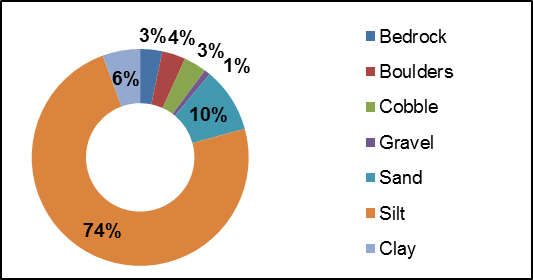
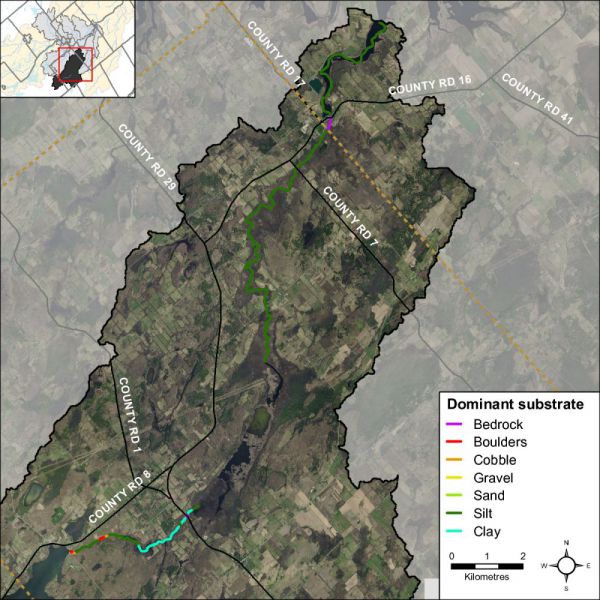
Diverse substrate is important for fish and benthic invertebrate habitat because some species have specific substrate requirements and for example will only reproduce on certain types of substrate. Figure 23 shows that 74 percent of the substrate observed on Irish Creek was dominated by silt and organic substrate consistent with wetland habitat conditions. Overall substrate conditions were fairly uniform along Irish Creek. Figure 24 shows the dominant substrate type observed for each section surveyed along Irish Creek.
Cobble and Boulder Habitat
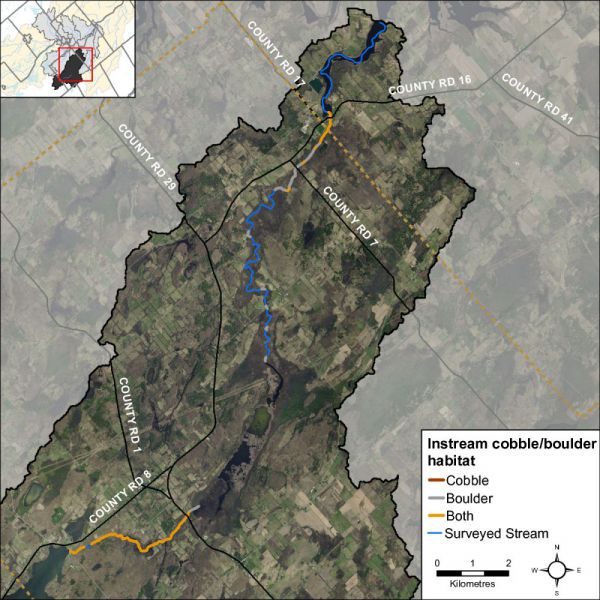
Boulders create instream cover and back eddies for large fish to hide and/or rest out of the current. Cobble provides important spawning habitat for certain fish species like walleye and various shiner species who are an important food source for larger fish. Cobble can also provide habitat conditions for benthic invertebrates that are a key food source for many fish and wildlife species. Figure 25 shows where cobble and boulder substrate are found in Irish Creek.
Instream Morphology
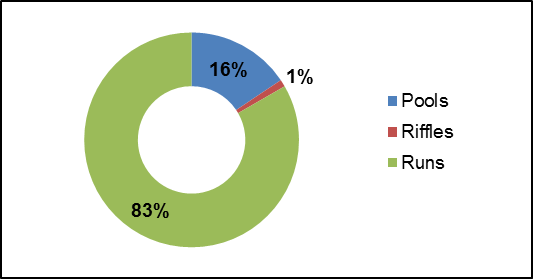
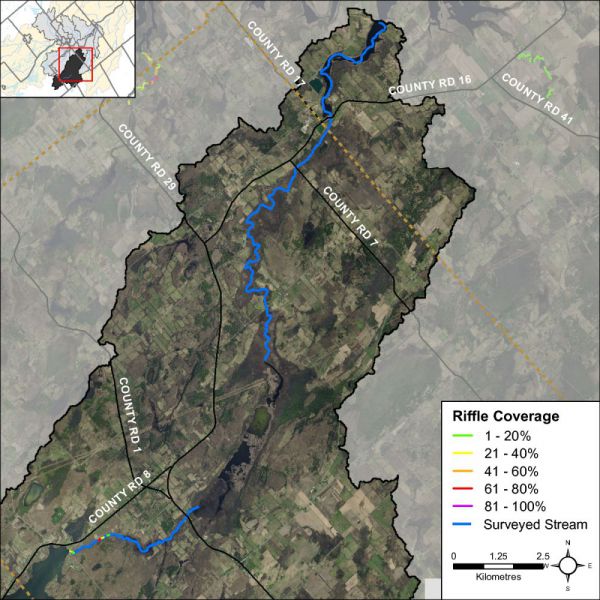
Pools and riffles are important habitat features for fish. Riffles are areas of agitated water and they contribute higher dissolved oxygen to the stream and act as spawning substrate for some species of fish, such as walleye. Pools provide shelter for fish and can be refuge pools in the summer if water levels drop and water temperature in the creek increases. Pools also provide important over wintering areas for fish. Runs are usually moderately shallow, with unagitated surfaces of water and areas where the thalweg (deepest part of the channel) is in the center of the channel. Figure 26 shows that Irish Creek is fairly uniform; 83 percent consists of runs, 1 percent riffles and 16 percent pools. Figure 27 shows where the limited areas of riffle habitat were observed along Irish Creek.
Vegetation Type
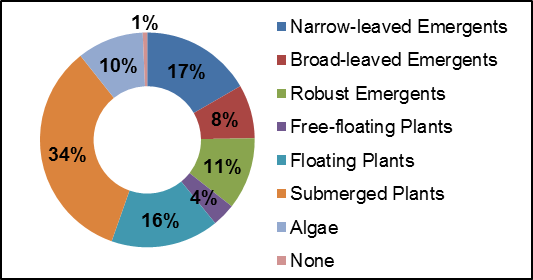
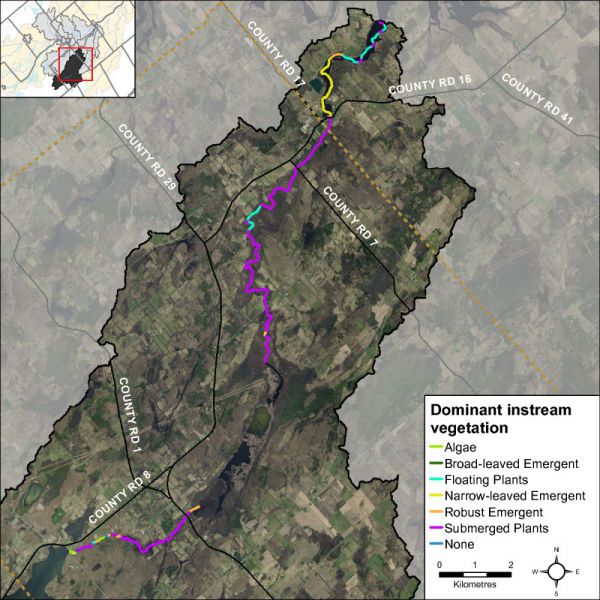
Instream vegetation provides a variety of functions and is a critical component of the aquatic ecosystem. For example emergent plants along the shoreline can provide shoreline protection from wave action and important rearing habitat for species of waterfowl. Submerged plants provide habitat for fish to find shelter from predator fish while they feed. Floating plants such as water lilies shade the water and can keep temperatures cool while reducing algae growth. The dominant vegetation type recorded at 34 percent consisted of submerged plants. Irish Creek had high levels of diversity for instream vegetation. Figure 28 depicts the plant community structure for Irish Creek. Figure 29 shows the dominant vegetation type observed for each section surveyed along Irish Creek.
Instream Vegetation Abundance
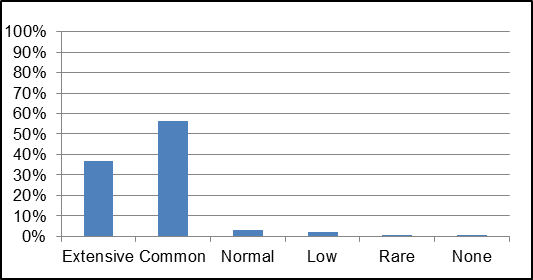
Instream vegetation is an important factor for a healthy stream ecosystem. Vegetation helps to remove contaminants from the water, contributes oxygen to the stream, and provides habitat for fish and wildlife. Too much vegetation can also be detrimental. Figure 30 demonstrates that Irish Creek had common and normal levels of instream vegetation for 60 percent of its length. Extensive vegetation levels were recorded at 37 percent of stream surveys, which can result in low oxygen levels along the system.
Invasive Species
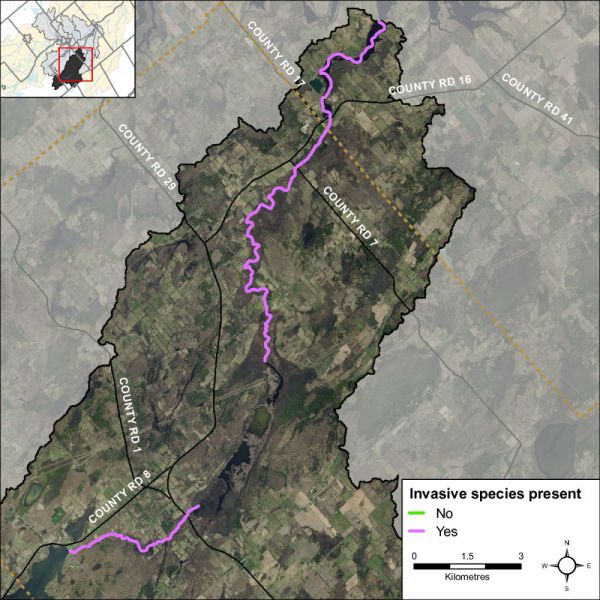
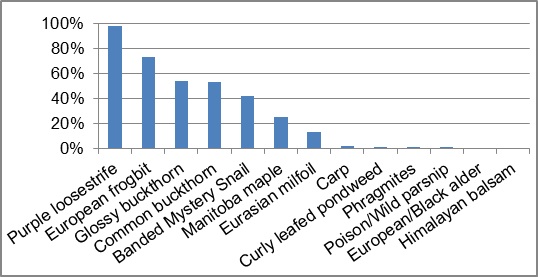
Invasive species can have major implications on streams and species diversity. Invasive species are one of the largest threats to ecosystems throughout Ontario and can out compete native species, having negative effects on local wildlife, fish and plant populations. One hundred percent of the sections surveyed along Irish Creek had invasive species (Figure 31). The invasive species observed in Irish Creek were European frogbit, purple loosestrife, glossy and common buckthorn, poison/wild parsnip, carp, banded mystery snail, curly leafed pondweed, Himalayan balsam, phragmites, European/Black alder, Eurasian milfoil and Manitoba maple. Figure 32 shows the frequency of the invasive species observed along Irish Creek.
Water Chemistry
During the stream characterization survey, a YSI probe is used to collect water chemistry information. Dissolved oxygen, conductivity and pH are measured at the start and end of each section.
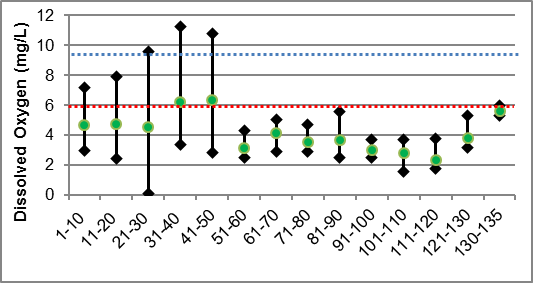
Dissolved Oxygen
Dissolved oxygen is a measure of the amount of oxygen dissolved in water. The Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines of the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME) suggest that for the protection of aquatic life the lowest acceptable dissolved oxygen concentration should be 6 mg/L for warmwater biota and 9.5 mg/L for coldwater biota (CCME, 1999). Figure 33 shows that the dissolved oxygen in Irish Creek was below the threshold for warmwater biota in most reaches of the system. The average dissolved oxygen levels observed within the main stem of Irish Creek was 4.19 mg/L which is below the recommended levels for warmwater biota.
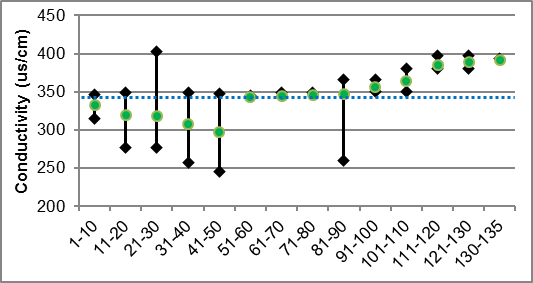
Conductivity
Conductivity in streams is primarily influenced by the geology of the surrounding environment, but can vary drastically as a function of surface water runoff. Currently there are no CCME guideline standards for stream conductivity; however readings which are outside the normal range observed within the system are often an indication of unmitigated discharge and/or stormwater input. The average conductivity observed within the main stem of Irish Creek was 345.8 µs/cm. Figure 34 shows the conductivity readings for Irish Creek.
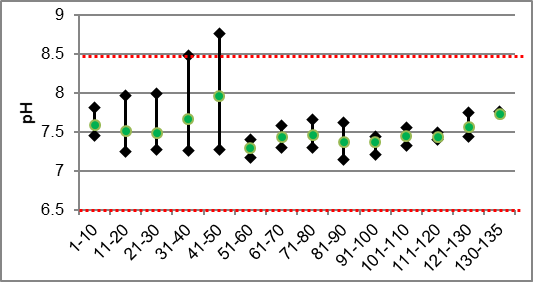
pH
Based on the PWQO for pH, a range of 6.5 to 8.5 should be maintained for the protection of aquatic life. Average pH values for Irish Creek averaged 7.52 thereby meeting the provincial standard (Figure 35).
Thermal Regime
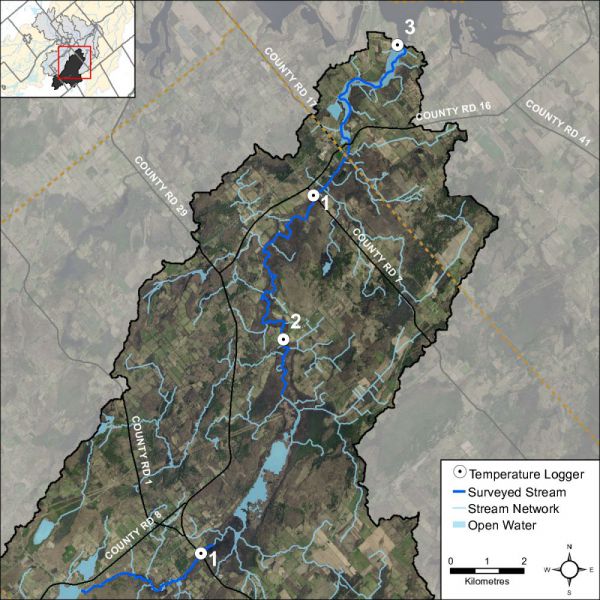
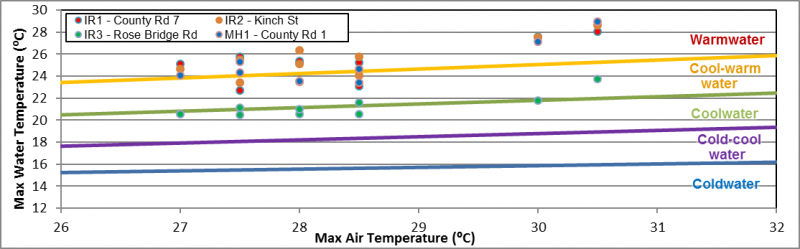
Many factors can influence fluctuations in stream temperature, including springs, tributaries, precipitation runoff, discharge pipes and stream shading from riparian vegetation. Water temperature is used along with the maximum air temperature (using the Stoneman and Jones method) to classify a watercourse as either warm water, cool water or cold water. Figure 36 shows where the thermal sampling sites were located along Irish Creek and Marshalls Creek. Analysis of the data collected indicates that Irish Creek is classified as a warm water system with cool water reaches (Figure 37).
| SITE ID | Y_WATER | X_AIR | CLASSIFICATION | PROGRAM | YEAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IR1 - County Rd 7 | 25.3 | 28.4 | WARMWATER | MACRO | 2014 |
| IR2 - Kinch St | 25.7 | 28.4 | WARMWATER | MACRO | 2014 |
| IR3 - Rose Bridge Rd | 21.3 | 28.4 | COOLWATER | MACRO | 2014 |
| MH1 - County Rd 1 | 24.9 | 0.0 | WARMWATER | MACRO | 2014 |
Each point on the graph represents a temperature that meets the following criteria:
- Sampling dates between July 1st and September 7th
- Sampling date is preceded by two consecutive days above 24.5 °C, with no rain
- Water temperatures are collected at 4pm
- Air temperature is recorded as the max temperature for that day
Groundwater
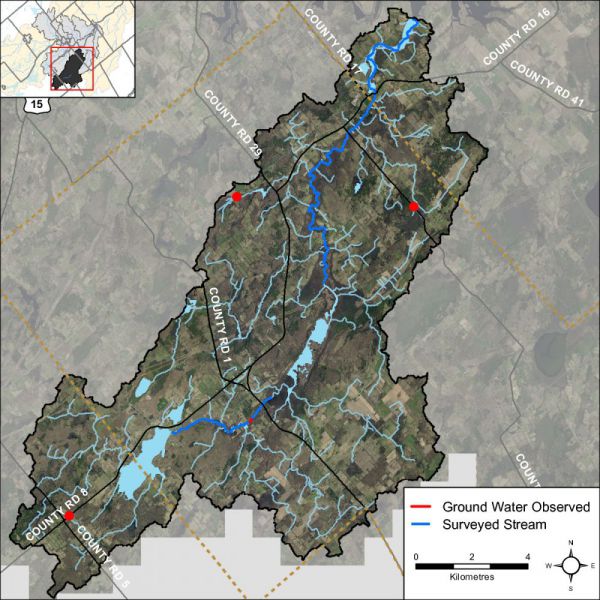
Groundwater discharge areas can influence stream temperature, contribute nutrients, and provide important stream habitat for fish and other biota. During stream surveys, indicators of groundwater discharge are noted when observed. Indicators include: springs/seeps, watercress, iron staining, significant temperature change and rainbow mineral film. Figure 38 shows areas where one or more of the above groundwater indicators were observed during stream surveys and headwater assessments.
Headwaters Drainage Features Assessment
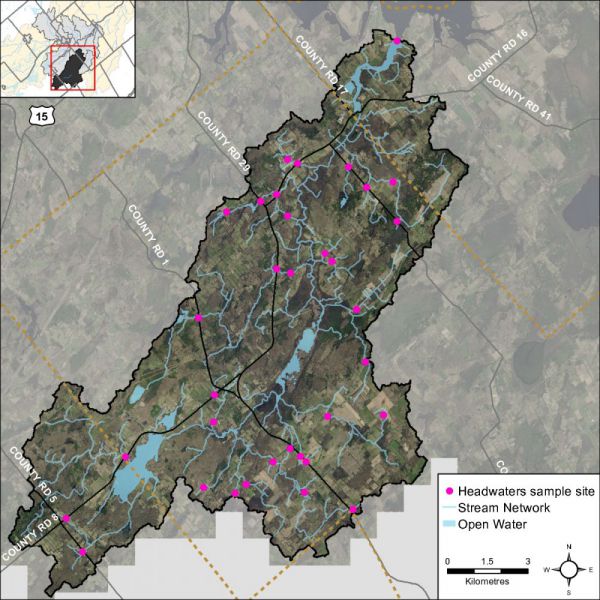
The RVCA Stream Characterization program assessed Headwater Drainage Features for the Middle Irish subwatershed in 2014. This protocol measures zero, first and second order headwater drainage features (HDF). It is a rapid assessment method characterizing the amount of water, sediment transport, and storage capacity within headwater drainage features (HDF). RVCA is working with other Conservation Authorities and the Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry to implement the protocol with the goal of providing standard datasets to support science development and monitoring of headwater drainage features. An HDF is a depression in the land that conveys surface flow. Additionally, this module provides a means of characterizing the connectivity, form and unique features associated with each HDF (OSAP Protocol, 2013). In 2014 the program sampled 34 sites at road crossings in the Irish Creek catchment area (Figure 39).
Feature Type
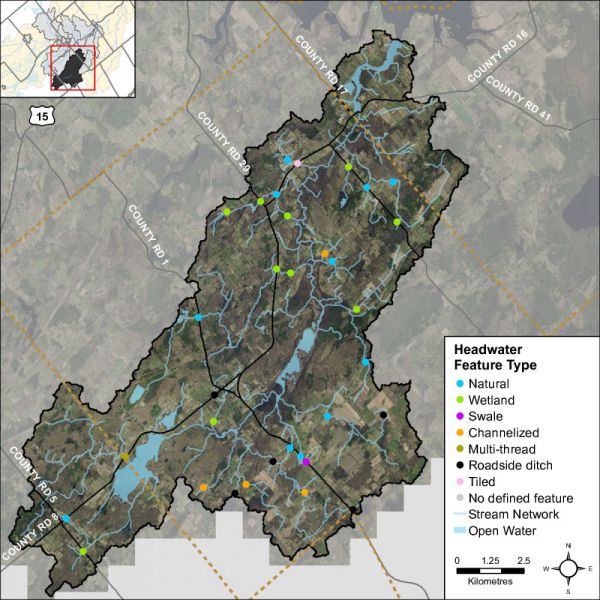
The headwater sampling protocol assesses the feature type in order to understand the function of each feature. The evaluation includes the following classifications: defined natural channel, channelized or constrained, multi-thread, no defined feature, tiled, wetland, swale, roadside ditch and pond outlet. By assessing the values associated with the headwater drainage features in the catchment area we can understand the ecosystem services that they provide to the watershed in the form of hydrology, sediment transport, and aquatic and terrestrial functions. The Irish Creek catchment is dominated by wetland and natural headwater drainage features. Four features were classified as having been channelized , five features were identified as roadside drainage features and one feature was tile drained. Figure 40 shows the feature type of the primary feature at the sampling locations.
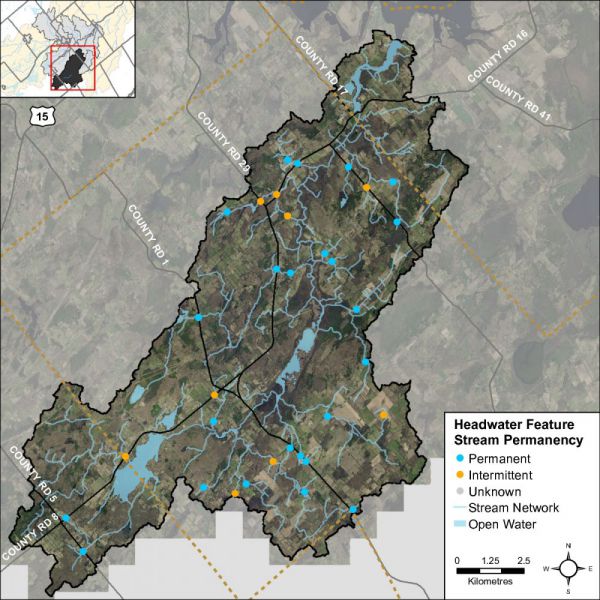
Headwater Feature Flow
The observed flow condition within headwater drainage features can be highly variable depending on timing relative to the spring freshet, recent rainfall, soil moisture, etc. Flow conditions are assessed in the spring and in the summer to determine if features are perennial and flow year round, if they are intermittent and dry up during the summer months or if they are ephemeral systems that do not flow regularly and generally respond to specific rainstorm events or snowmelt. Flow conditions in headwater systems can change from year to year depending on local precipitation patterns. Figure 41 shows the observed flow conditions at the sampling locations in the Irish Creek catchment in 2014.
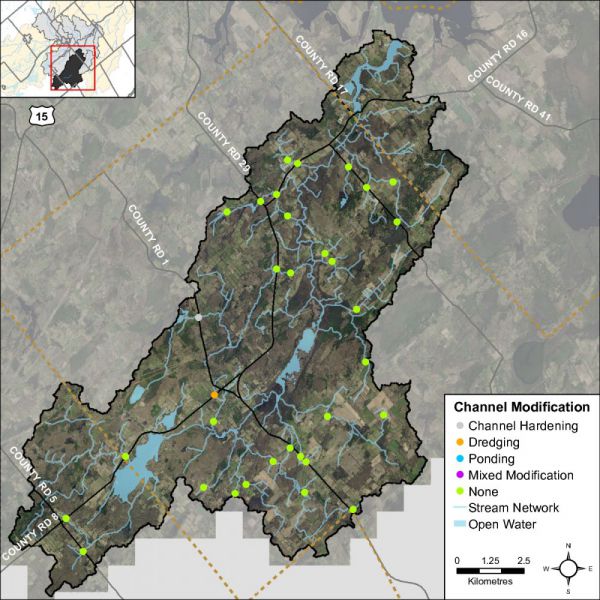
Feature Channel Modifications
Channel modifications were assessed at each headwater drainage feature sampling location. Modifications include channelization, dredging, hardening and realignments. The majority of sampling locations for the Irish Creek catchment area were classified as having no channel modifications, one channel was classified as being hardened and one appeared to have been historically dredged. Figure 42 shows the channel modifications observed at the sampling locations for Irish Creek.
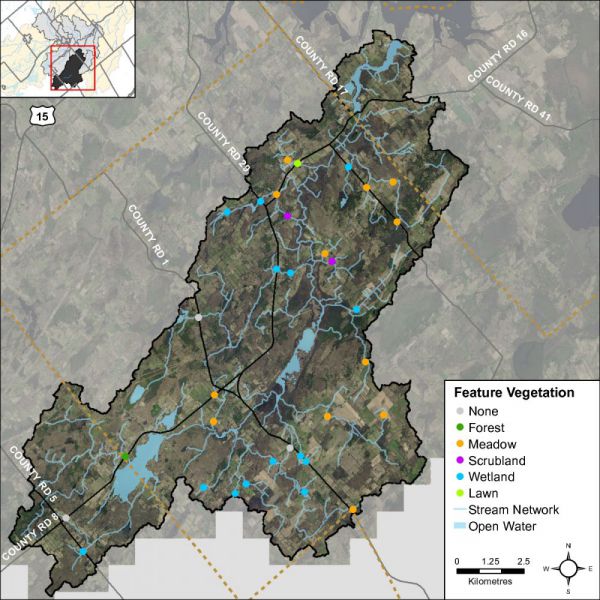
Headwater Feature Vegetation
Headwater feature vegetation evaluates the type of vegetation that is found within the drainage feature. The type of vegetated within the channel influences the aquatic and terrestrial ecosystem values that the feature provides. For some types of headwater features the vegetation within the feature plays a very important role in flow and sediment movement and provides wildlife habitat. The following classifications are evaluated no vegetation, lawn, wetland, meadow, scrubland and forest. The features assessed in the Irish Creek catchment were classified being dominated by wetland, scrubland, meadow and forest. One feature was classified as having lawn. Figure 43. Depicts the dominant vegetation observed at the sampled headwater sites in the Irish Creek catchment.
Headwater Feature Riparian Vegetation
Headwater riparian vegetation evaluates the type of vegetation that is found along the adjacent lands of a headwater drainage feature. The type of vegetation within the riparian corridor influences the aquatic and terrestrial ecosystem values that the feature provides to the watershed. The sample locations in Irish Creek were dominated by natural vegetation in the form of meadow, scrubland, forest and wetland vegetation. Figure 44. Depicts the type of riparian vegetation observed at the sampled headwater sites in the Irish Creek catchment.
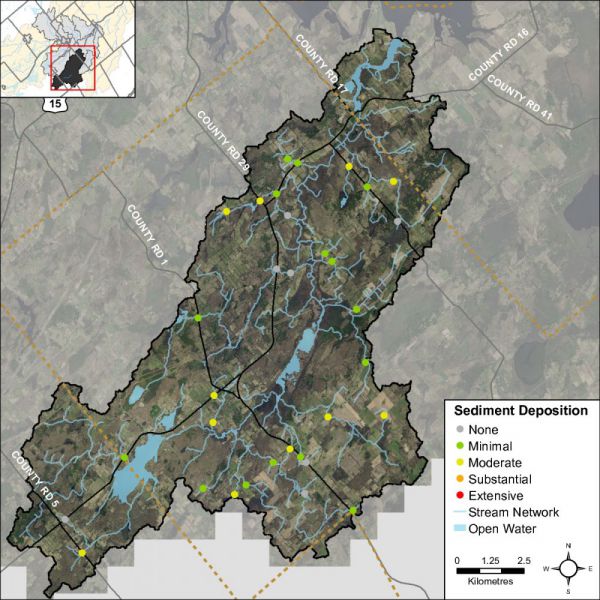
Headwater Feature Sediment Deposition
Assessing the amount of recent sediment deposited in a channel provides an index of the degree to which the feature could be transporting sediment to downstream reaches (OSAP, 2013). Evidence of excessive sediment deposition might indicate the requirement to follow up with more detailed targeted assessments upstream of the site location to identify potential best management practices to be implemented. Conditions ranged from no deposition observed to moderate deposition recorded. Figure 45. Depicts the degree of sediment deposition observed at the sampled headwater sites in the Irish Creek catchment.
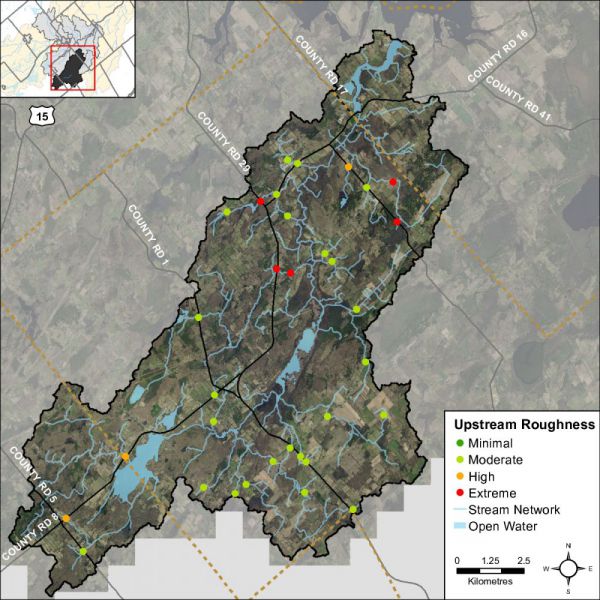
Headwater Feature Upstream Roughness
Feature roughness will provide a measure of the amount of materials within the bankfull channel that could slow down the velocity of water flowing within the headwater feature (OSAP, 2013). Materials on the channel bottom that provide roughness include vegetation, woody debris and boulders/cobble substrates. Roughness can provide benefits in mitigating downstream erosion on the headwater drainage feature and the receiving watercourse by reducing velocities. Roughness also provides important habitat conditions to aquatic organisms. The sample locations in the Irish Creek catchment area ranged from moderate to extreme roughness conditions. Figure 46 shows the feature roughness conditions at the sampling locations in the Irish Creek catchment.
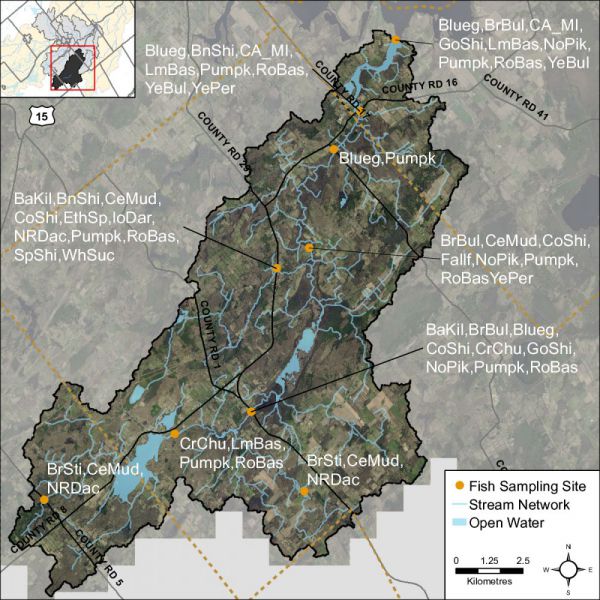
Fish Community
The Irish Creek catchment is classified as a mixed community of warm and cool water recreational and baitfish fishery with 22 species observed. Table 8 lists those species observed in the catchment (Source: MNR/RVCA). Figure 47 shows the sampling locations along Irish Creek.
| Fish Species | Fish code | Fish Species | Fish code | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| banded killifish | BaKil | golden shiner | GoShi | ||||||
| blacknose shiner | BnShi | iowa darter | IoDar | ||||||
| bluegill | Blueg | largemouth bass | LmBas | ||||||
| brook stickleback | BrSti | northern pike | NoPik | ||||||
| brown bullhead | BrBul | northern redbelly dace | NRDac | ||||||
| carps and minnows | CA_MI | pumpkinseed | Pumpk | ||||||
| central mudminnow | CeMud | rock bass | RoBas | ||||||
| common shiner | CoShi | spotfin shiner | SpShi | ||||||
| creek chub | CrChu | white sucker | WhSuc | ||||||
| etheostoma sp. | Ethsp | yellow bullhead | YeBul | ||||||
| fallfish | Fallf | yellow perch | YePer |
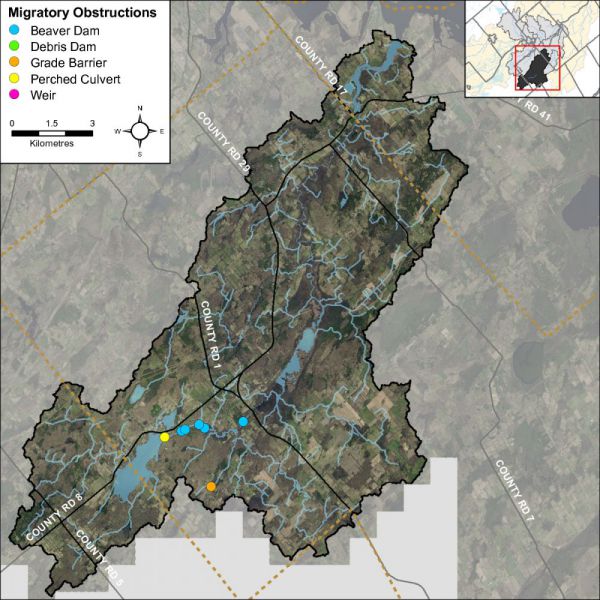
Migratory Obstructions
It is important to know locations of migratory obstructions because these can prevent fish from accessing important spawning and rearing habitat. Migratory obstructions can be natural or manmade, and they can be permanent or seasonal. Figure 48 shows that Irish Creek had multiple beaver dams, one perched culvert and one grade barrier at the time of the survey in 2014.
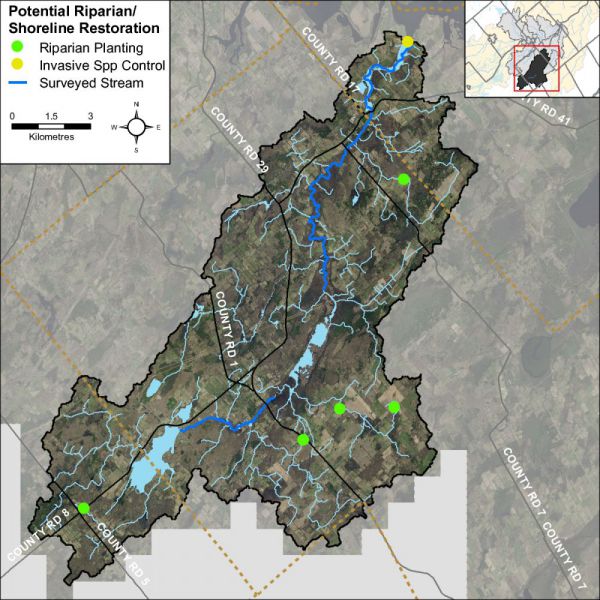
Riparian Restoration
Figure 49 depicts the location of a riparian restoration opportunity as a result of observations made during the stream survey and headwater drainage feature assessments.